Forests are an important component of the Nordic natural and societal ecosystem, providing ecosystem services (such as storing and filtering of water), timber for commercial products, and rural employment. However, these ecosystems are threatened by an invasive bark beetle pest that can significantly harm the forests.
At CollectiveCrunch, we offer sophisticated AI-based modeling utilizing satellite data, to identify bark beetle outbreaks at an early stage. The system has been in use by several of our customers, in particular Metsä Group and its co-operative members.
So far the use case centered around early response to outbreaks during the season from approximately May to October. However, these models can also be used to focus winter harvesting on bark beetle risk areas. With this approach, the year-round harvest planning factors in bark beetle risks and therefore reduces the overall impact of bark beetles.

In this article, we’ll explore the importance of monitoring and managing bark beetle infestations, the advantages of using our advanced mapping tools, and how proactive measures contribute to sustainable forestry and forest ecosystem protection.
Understanding Bark Beetles and Their Threat to Forests
What is a Bark Beetle?
Bark beetles are small insects that burrow into the bark of trees, disrupting their ability to transport water and nutrients. While they play a natural role in forest cycles by targeting weakened trees, their populations can explode under certain conditions, leading to widespread bark beetle damage.
The Purpose and Impact of Bark Beetles
In a balanced ecosystem, bark beetles help recycle nutrients by breaking down dead or dying trees. However, climate change, drought, and other stressors can lead to infestations that kill healthy trees, drastically altering the forest ecosystem and reducing forest biodiversity.
Economic and Environmental Impact of Bark Beetle Infestations
Bark beetle outbreaks can have a severe economic impact on forestry: Damaged timber leads to financial losses, while increased forest management costs strain resources. Additionally, the environmental impact of pest control methods, if not managed carefully, can harm non-target species and further destabilize ecosystems.
Why Winter Harvest Planning is Crucial?
Bark beetles become less active during harsh winter conditions, offering a strategic opportunity for forest management. Traditionally, winter harvests have been conducted without specifically accounting for bark beetle infestations. However, by incorporating bark beetle presence and risk into winter harvest planning, forest managers can significantly reduce the likelihood of outbreaks in the following season.
Using our advanced bark beetle maps, you can identify areas at high risk of infestation and target them during the winter harvest. This proactive approach disrupts the pest’s lifecycle, mitigates potential damage, and ensures a healthier forest ecosystem.
Benefits of Using Bark Beetle Maps
1. Accurate Pest Detection
With the help of AI-tailored bark beetle models, we offer detailed information on infestation areas. If you are aware of the affected regions on time, you can adopt the bark beetle control measures early and significantly reduce losses of forest and value.
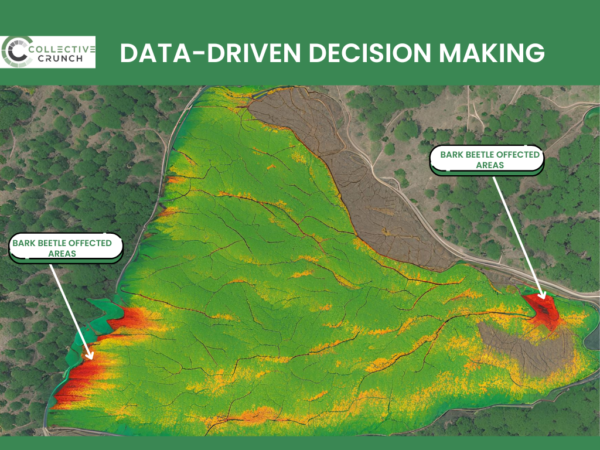
2. Data-Driven Decision Making
When forest managers have accurate information on the location and activity of bark beetles, they can schedule when and where to harvest the forest. This way of working is less wasteful of resources and destroys fewer desirable trees due to misinformation and confusion.
3. Optimised Winter Harvest Operations
Winter harvesting is a critical time for managing bark beetle infestations effectively. With the insights provided by our bark beetle maps, you can pinpoint high-risk areas and plan harvests more efficiently. This ensures the removal of infested trees while preserving healthy ones, ultimately improving timber quality and reducing economic losses caused by pest damage.
4. Strengthening Forest Resilience
Using our tools to manage bark beetle infestations promotes forests’ overall health and resilience. Controlling outbreaks and maintaining tree diversity create a balanced ecosystem that is less prone to future pest attacks. This aligns with long-term goals for sustainable forestry and enhances the stability of forest ecosystems in the face of changing environmental conditions.
Proactive Pest Management: Key Strategies
Early Detection and Monitoring:
Regular monitoring using our bark beetle maps ensures that infestations are caught early. This reduces the need for widespread interventions and lowers the overall environmental impact of pest control measures.
Restoration and Reforestation
Post-harvest, restoring affected areas through reforestation helps maintain forest biodiversity and ecosystem services. Planting diverse tree species can also increase resilience against future infestations.
Public Awareness and Collaboration
Engaging with local communities and stakeholders is crucial for comprehensive forest management. Educating them on how to get rid of bark beetles and the importance of proactive measures fosters collective action to protect forests.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Disease is Spread by Bark Beetles?
They are often associated with the spread of blue-stain fungi. This fungus clogs the tree’s vascular system, exacerbating the damage caused by the beetles and leading to faster tree mortality.
How Do I Identify Bark Beetle Damage?
Signs of bark beetle damage include small, round exit holes in the bark, sawdust-like frass around the base of the tree, and discolored or thinning foliage. Early detection is critical for effective management.
How Can Our Bark Beetles Maps Help You?
Our maps provide a comprehensive view of infestation hotspots, allowing you to take immediate action. With this data, you can prioritize interventions, plan efficient harvests, and reduce the long-term impact of pests on your forests.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Forest’s Future
Bark beetles pose a significant threat to forest health, but their impact can be mitigated with the right tools and strategies. CollectiveCrunch’s bark beetles maps offer a powerful solution for forest managers, combining advanced AI with actionable insights to support sustainable forestry practices. By leveraging our technology to plan your winter season harvests, you can protect your forests, enhance their resilience, and contribute to a healthier planet.
Ready to safeguard your forests? Contact us today to learn more about our maps and other innovative tools for sustainable forest management